Renal Masses
What are the common renal masses?
- Simple renal cysts
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Poly cystic kidney disease
- Abscess
What are the useful imaging modalities used to investigate a renal mass?
- Ultrasonography
- The initial imaging procedure of choice, US can distinguish between a cyst and from a solid mass. Three major criteria for a single simple cyst on ultrasound are:
- the mass is round and sharply demarcated with smooth walls
- no echoes (anechoic) within mass
- strong posterior wall echo indicating good sound transmission through the cyst
- No further evaluation is necessary if all of these criteria are satisfied, since the likelihood of malignancy is small.
- If US equivocal (complex cyst), or suggestive of malignancy
- solid or complex
- with internal echoes
- and irregular walls
- if calcifications or septae are seen
- if multiple cysts are clustered so that they may be masking underlying carcinoma
- Then proceed to CT
- The initial imaging procedure of choice, US can distinguish between a cyst and from a solid mass. Three major criteria for a single simple cyst on ultrasound are:
- CT
- A renal CT scan, both with and without IV contrast, is the next appropriate step.
- It has replaced the renal arteriography as the next diagnostic step.
- CT is as accurate as, and obviates the potential morbidity of, angiography in defining the renal mass.
- Also, CT can give information about local staging to allow definitive surgical management if needed.
- MRI
- MRI is used to evaluate solid tumors seen on CT if a patient is unable to receive IV contrast.
- Vascular invasion, IVC thrombi are demonstrated without IV contrast.

What are the pathological characteristics of renal cancer?
- Mass in kidney
- Propensity to invade renal vein and inferior vena cava
- Tumor can extend to perirenal structures - nodes
What are the useful imaging procedures in patients suspected to have renal cell carcinoma?
We will discuss the primary tumor and not investigation of metastatic lesions.
- Primary tumor
- CT is the diagnostic procedure of choice. It can provide information about the mass, perirenal extension, vascular invasion, nodal and liver involvement.
- US: Serves as a screening test to diagnose renal cysts.
- MR: Useful to evaluate vascular invasion by the tumor.
- IVP and angiogram are rarely used now.
- Metastatic workups
What are the imaging manifestations of renal carcinoma?
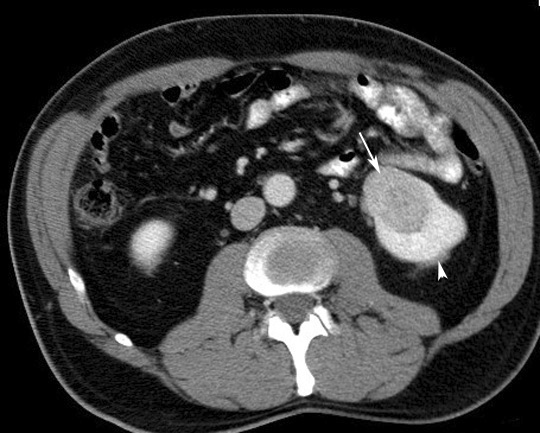
- CT
- Hypodense unless it is hemorrhagic
- Cystic mass
- Calcified mass
- Most enhance after contrast administration, but less than normal kidney enhancement
- Thickened or irregular walls of cystic portion
- Thickened or enhanced septae within the cystic mass
- A multilocular mass
- Invasion of renal vein and IVC
- Nodes