Mental status changes
Q1: What are the common intra cranial causes for mental status changes?
Mental status changes often are due to toximetabolic causes (drugs, dehydration, infection, liver or kidney dysfunction) and resolve when the underlying condition is treated. If mental status changes persist, or in presence of other factors (headache, head trauma, focal neuro deficits), a brain scan, preferably an MRI, is indicated.
Mental status changes-Cases
Case1:
A 20 year old Type I diabetic male has a period of weakness, polyuria, and polydipsia, followed by mental status changes. You discover that he has not taken his insulin as scheduled. Labs show serum glucose of 600 and high anion gap metabolic acidosis. Urine tests show glycosuria and ketonuria.
- Are imaging procedures necessary for this patient? If so, what would you order?
- What is your diagnosis?
Case 2:.
A 70-year-old male is in a minor car accident in which he thinks he might have bumped his head. A few weeks later he develops a mild but constant headache followed by bouts of confusion.
- Are imaging procedures necessary for this patient? If so, what would you order?
- What is your diagnosis?
- Sub acute subdural hematoma
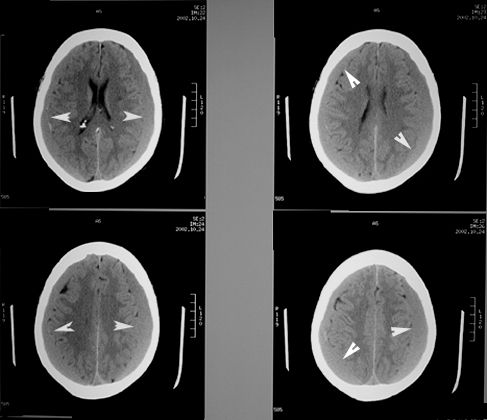 |
Bilateral Subacute Subdural Hematoma
- These are bilateral and are isodense with the brain because of gradual loss of density of blood.
- On close exam you see that the sulcal markings do not reach the surface of the skull, due to the intervening subdural collection.
- Arrowheads point to subdurals separating the brain surface markings from the skull.
- There is no midline shift.
|
Case 3:
40-year old lady with a history of breast carcinoma diagnosed 6 years ago, presented with headache, ataxia, progressive memory problems and changes in her personality.
- Are imaging procedures necessary for this patient? If so, what would you order?
- If this patient's condition were severe or rapidly deteriorating in the ER, a CT would likely be performed first.
- If she presented to the outpatient clinic with a sub acute presentation, a MRI is the study of choice for her probable condition.
- What is your diagnosis?
|
Multiple Metastasis To The Brain From Breast Primary
40-year old lady with a history of breast carcinoma diagnosed 6 years ago, presented with headache and ataxia.
Findings: Shower of at least 30 metastatic enhancing lesions are seen closely packed together within both cerebellar hemispheres (yellow arrows), and few lesions also seen within both posterior fronto-parietal lobes (red arrows). |

